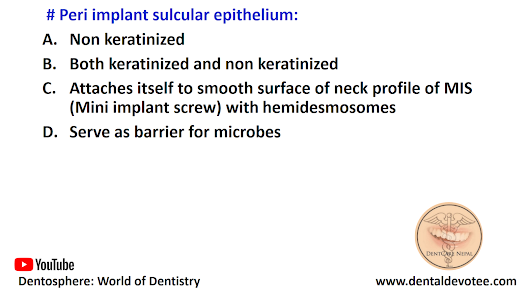
# Peri implant sulcular epithelium:
A. Non keratinized
B. Both keratinized and non keratinized
C. Attaches itself to smooth surface of neck profile of MIS (Mini implant screw) with hemidesmosomes
D. Serve as barrier for microbes
The correct answer is: A. Non keratinized.
After 3 months, all implants were firmly anchored in the bone and had no clinical signs of peri-implant inflammation. Undecalcified histologic sections demonstrated that all implants achieved osseointegration with direct bone contact.
• The epithelial structures showed a peri-implant sulcus with a non-keratinized sulcular epithelium and a junctional epithelium.
• Ultrastructural examination of the long junctional epithelial attachment adjacent to dental implants has demonstrated that epithelial cells attach with a basal lamina and hemidesmosomes.
• Note that the intrasulcular tissue appears more erythematosus as the result of the thin, nonkeratinized layer of epithelium overlying the connective tissue.